Former Obleserlab postdoc Molly Henry with Björn Herrmann and Jonas Obleser has a new publication in press at Journal of Neuroscience.
Neural microstates govern perception of auditory input without rhythmic structure
by Henry, MJ, Hermann, B, Obleser, J (in press). J Neurosci.
In deviation from Molly’s former paradigms, we here aimed at better understanding the role of oscillatory (as well as non-oscillatory) slow neural activity in shaping auditory perception when the stimulus is devoid of any rhythmic structure.
For a change, the significance statement and a teaser figure are shown below.
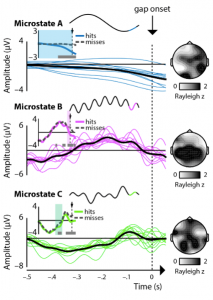
Abstract
Our ability to hear faint sounds fluctuates together with slow brain activity that synchronizes with environmental rhythms. However, it is so far not known how brain activity at different time scales might interact to influence perception when there is no rhythm with which brain activity can synchronize. Here, we used electroencephalography (EEG) to measure brain activity while participants listened for short silences that interrupted ongoing noise. We examined brain activity in three different frequency bands: delta, theta, and alpha. Participants’ ability to detect gaps depended on different numbers of frequency bands — sometimes one, two, or three — at different times. Changes in the number of frequency bands that predict perception are a hallmark of a complex neural system.

