May I humbly point you to three new articles I had the honour to be involved in recently.
Firstly, Chris Petkov, Nikos Logothetis and I have put together a very broad overview over what we think is the current take on processing streams of voice, speech and, more generally, vocalisation input in primates. It appears in THE NEUROSCIENTIST and is aimed at (sic) neuroscientists who are not in the language and audition field on an everyday basis. It goes back all the way to Wernicke and also owes a lot to the hard work on functional and anatomical pathways in the primate brain by people like Jon Kaas, Troy Hackett, Josef Rauschecker, or Jeffrey Schmahmann.
Secondly, Angela Friederici, Sonja A. Kotz, Sophie Scott and myself have a new article in press in HUMAN BRAIN MAPPING where we have tried and disentangled the grammatical violation effects in speech that Angela had observed earlier in the anterior superior temporal gyrus and the effects of speech intelligibility Sophie had clearly pinpointed in the sulcus just below. When combining these two manipulations into one experimental framework, the results turned out surprisingly clear-cut! Also, an important finding on the side: While the activations we observed are of course bilateral, any kind of true interaction of grammar and intelligibility were located in the left hemisphere (both in inferior frontal and in superior temporal areas). Watch out here for the upcoming pre-print.
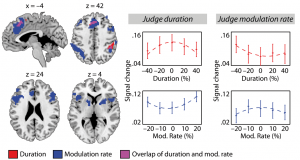
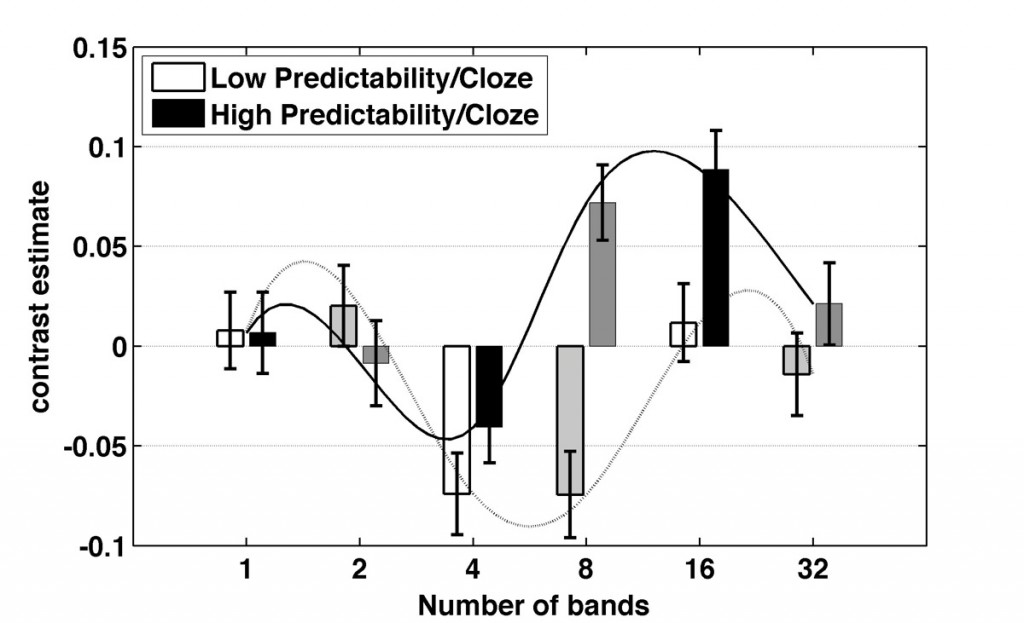
Finally, recent data by Sonja Kotz and I have somewhat scrutinised the way I see the the interplay of the anterior and posterior STS, as well as the IFG and, importantly, the left angular gyrus (see the figure below showing the response behaviour of the left angular gyrus over various levels of degradation as well as semantic expectancy, with pooled data from the current as well as a previous study in J Neurosci by Obleser et al., 2007). These data, on a fine-tuned cloze-probability manipulation to sentences of varying degradation are available now in CEREBRAL CORTEX. Thanks for you interest, and let me know what you think.
References
- Petkov CI, Logothetis NK, Obleser J. Where are the human speech and voice regions, and do other animals have anything like them? Neuroscientist. 2009 Oct;15(5):419–29. PMID: 19516047. [Open with Read]
Modern lesion and imaging work in humans has been clarifying which brain regions are involved in the processing of speech and language. Concurrently, some of this work has aimed to bridge the gap to t […]
- Friederici AD, Kotz SA, Scott SK, Obleser J. Disentangling syntax and intelligibility in auditory language comprehension. Hum Brain Mapp. 2010 Mar;31(3):448–57. PMID: 19718654. [Open with Read]
Studies of the neural basis of spoken language comprehension typically focus on aspects of auditory processing by varying signal intelligibility, or on higher-level aspects of language processing such […]
- Obleser J, Kotz SA. Expectancy constraints in degraded speech modulate the language comprehension network. Cereb Cortex. 2010 Mar;20(3):633–40. PMID: 19561061. [Open with Read]
In speech comprehension, the processing of auditory information and linguistic context are mutually dependent. This functional magnetic resonance imaging study examines how semantic expectancy (“cloze […]