We are proud to publish our recent study on how network dynamics of beta-band oscillations in the human brain mediate response speed in auditory perceptual decision-making. This work will appear soon in the first volume of the promising journal Network Neuroscience.
Pre-print link http://biorxiv.org/content/early/2016/12/19/095356
Abstract
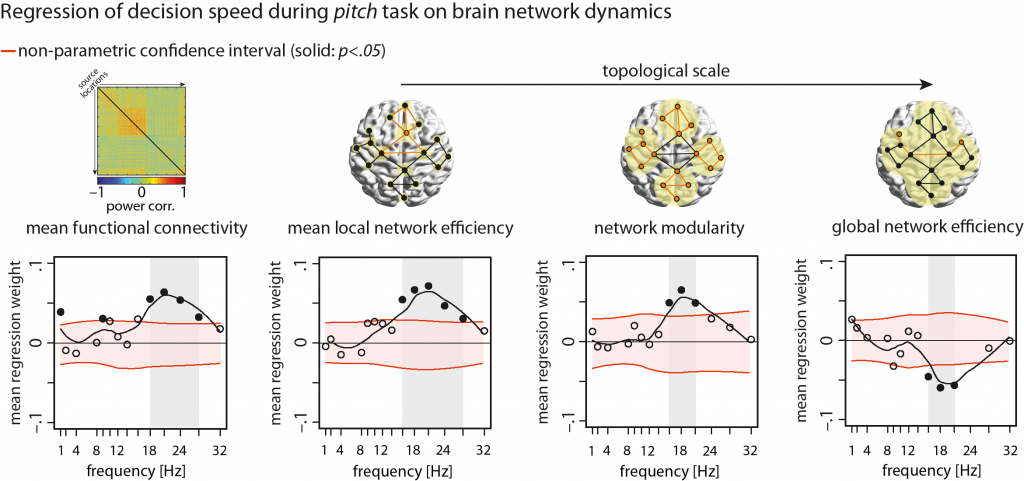
Perceptual decisions vary in the speed at which we make them. Evidence suggests that translating sensory information into behavioral decisions relies on distributed interacting neural populations, with decision speed hinging on power modulations of neural oscillations. Yet, the dependence of perceptual decisions on the large-scale network organization of coupled neural oscillations has remained elusive. We measured magnetoencephalography signals in human listeners who judged acoustic stimuli made of carefully titrated clouds of tone sweeps. These stimuli were used under two task contexts where the participants judged the overall pitch or direction of the tone sweeps. We traced the large-scale network dynamics of source-projected neural oscillations on a trial-by-trial basis using power envelope correlations and graph-theoretical network discovery. Under both tasks, faster decisions were predicted by higher segregation and lower integration of coupled beta-band (~16–28 Hz) oscillations. We also uncovered brain network states that promoted faster decisions and emerged from lower-order auditory and higher-order control brain areas. Specifically, decision speed in judging tone-sweep direction critically relied on nodal network configurations of anterior temporal, cingulate and middle frontal cortices. Our findings suggest that global network communication during perceptual decision-making is implemented in the human brain by large-scale couplings between beta-band neural oscillations. 
