Auditory Cognition’s own Malte Wöstmann is in press in Cerebral Cortex with his latest offering on how attentional control manifests in alpha power changes: Ignoring speech can be beneficial (if comprehending speech potentially detracts from another task), and we here show how this change in listening goals turns around the pattern of alpha-power changes with changing speech degradation. (We will update as the paper becomes available online.)
Wöstmann, M., Lim, S.J., & Obleser, J. (2017). The human neural alpha response to speech is a proxy of attentional control. Cerebral Cortex. In press.
Abstract
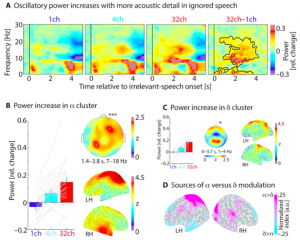
Human alpha (~10 Hz) oscillatory power is a prominent neural marker of cognitive effort. When listeners attempt to process and retain acoustically degraded speech, alpha power enhances. It is unclear whether these alpha modulations reflect the degree of acoustic degradation per se or the degradation-driven demand to a listener’s attentional control. Using an irrelevant-speech paradigm in electroencephalography (EEG), the current experiment demonstrates that the neural alpha response to speech is a surprisingly clear proxy of top-down control, entirely driven by the listening goals of attending versus ignoring degraded speech. While (n=23) listeners retained the serial order of 9 to-be-recalled digits, one to-be-ignored sentence was presented. Distractibility of the to-be-ignored sentence parametrically varied in acoustic detail (noise-vocoding), with more acoustic detail of distracting speech increasingly disrupting listeners’ serial memory recall. Where previous studies had observed decreases in parietal and auditory alpha power with more acoustic detail (of target speech), alpha power here showed the opposite pattern and increased with more acoustic detail in the speech distractor. In sum, the neural alpha response reflects almost exclusively a listener’s exertion of attentional control, which is decisive for whether more acoustic detail facilitates comprehension (of attended speech) or enhances distraction (of ignored speech).

