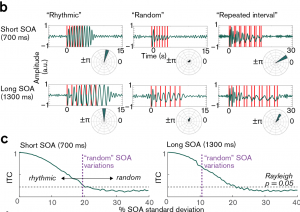
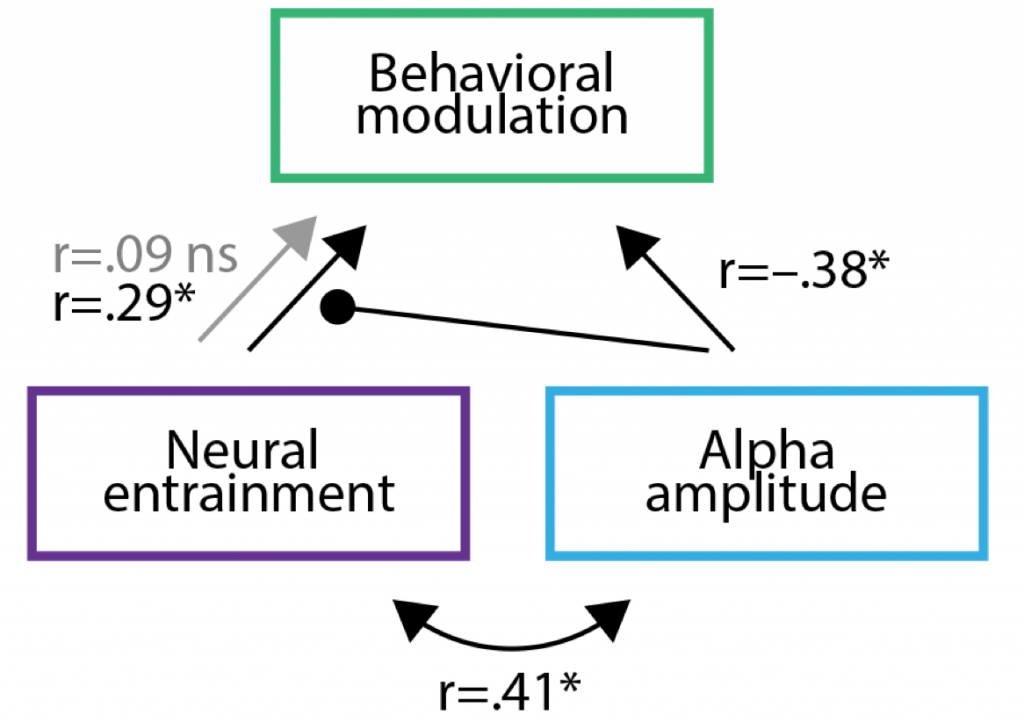
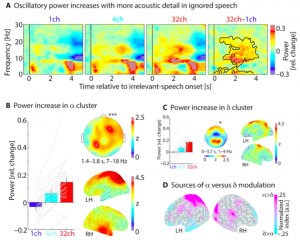
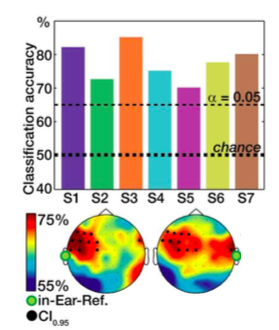
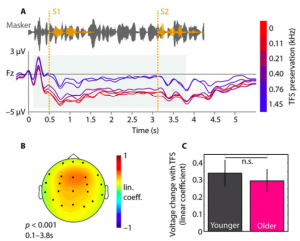
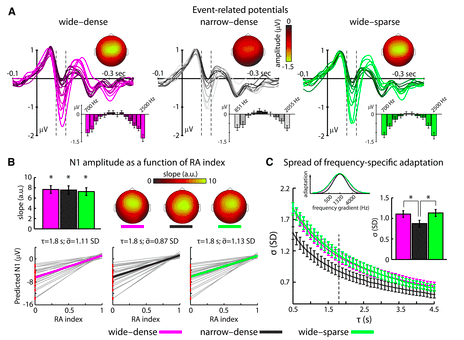
My colleagues and collaborator Peter Lakatos and Molly Henry and I took to our desks and Matlab consoles, when Assaf Breska and Leon Deouell came out earlier this year with their paper in Plos Biology.
We had a few things to say about what we then perceived as a rather pessimistic assessment of neural entrainment. However, since then a great and quite frutiful discussion has emerged, now published in Plos Biology:
Meanwhile, Breska and Deouell added some more behavioural data and replied to us (now also published).
— Enjoy!