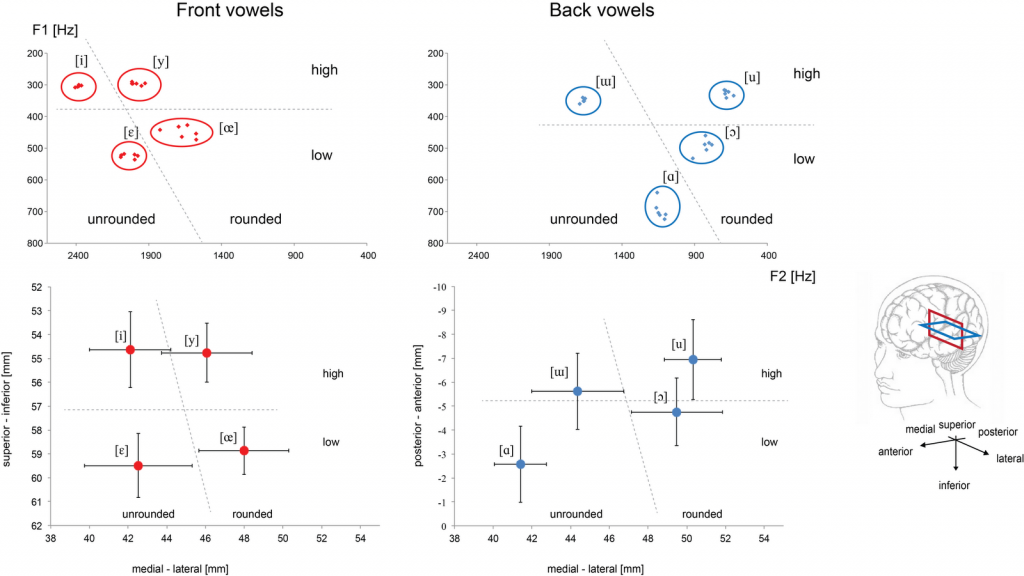
Phonetic cues instantaneously mapped onto dialectal categories appear to be extracted at early moments in auditory speech perception, as we try to show in our paper
You had me at “Hello”: Rapid extraction of dialect information from spoken words
to appear in NeuroImage (Mathias Scharinger, Philip Monahan, William Idsardi).
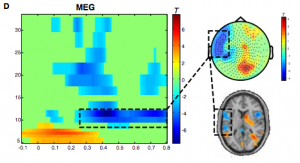
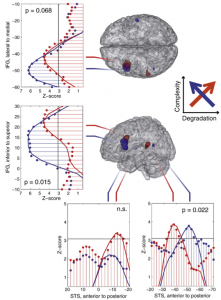
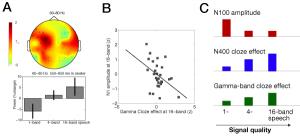
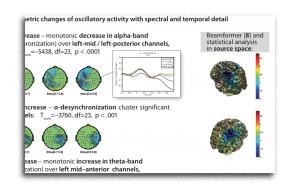
In a modified passive oddball design, we compare the Mismatch Negativity (MMN) to deviants in one American English dialect (Standard American English or African-American Vernacular English) to the standards of the respective other dialect. In a control condition, deviants within the same dialects have the same averaged acoustic distance to their standards than the cross-dialectal averaged acoustic distance. Standards and deviants were always spoken exemplars of ‘Hello’ in both dialects (ca. 500 ms). MMN effects are significant in the cross-dialectal condition only, implying that a pure acoustic standard-deviant distance is not sufficient to elicit substantial mismatch effects. We interpret these findings, together with N1m source localization data, as evidence for a rapid extraction of dialect information via salient acoustic-phonetic cues. From the location and orientation of the N1m source activity, we can infer that dialect switches from standards to deviants engage areas in superior temporal sulcus/gyrus.
References
- Scharinger M, Monahan PJ, Idsardi WJ. You had me at “Hello”: Rapid extraction of dialect information from spoken words. Neuroimage. 2011 Jun 15;56(4):2329–38. PMID: 21511041. [Open with Read]