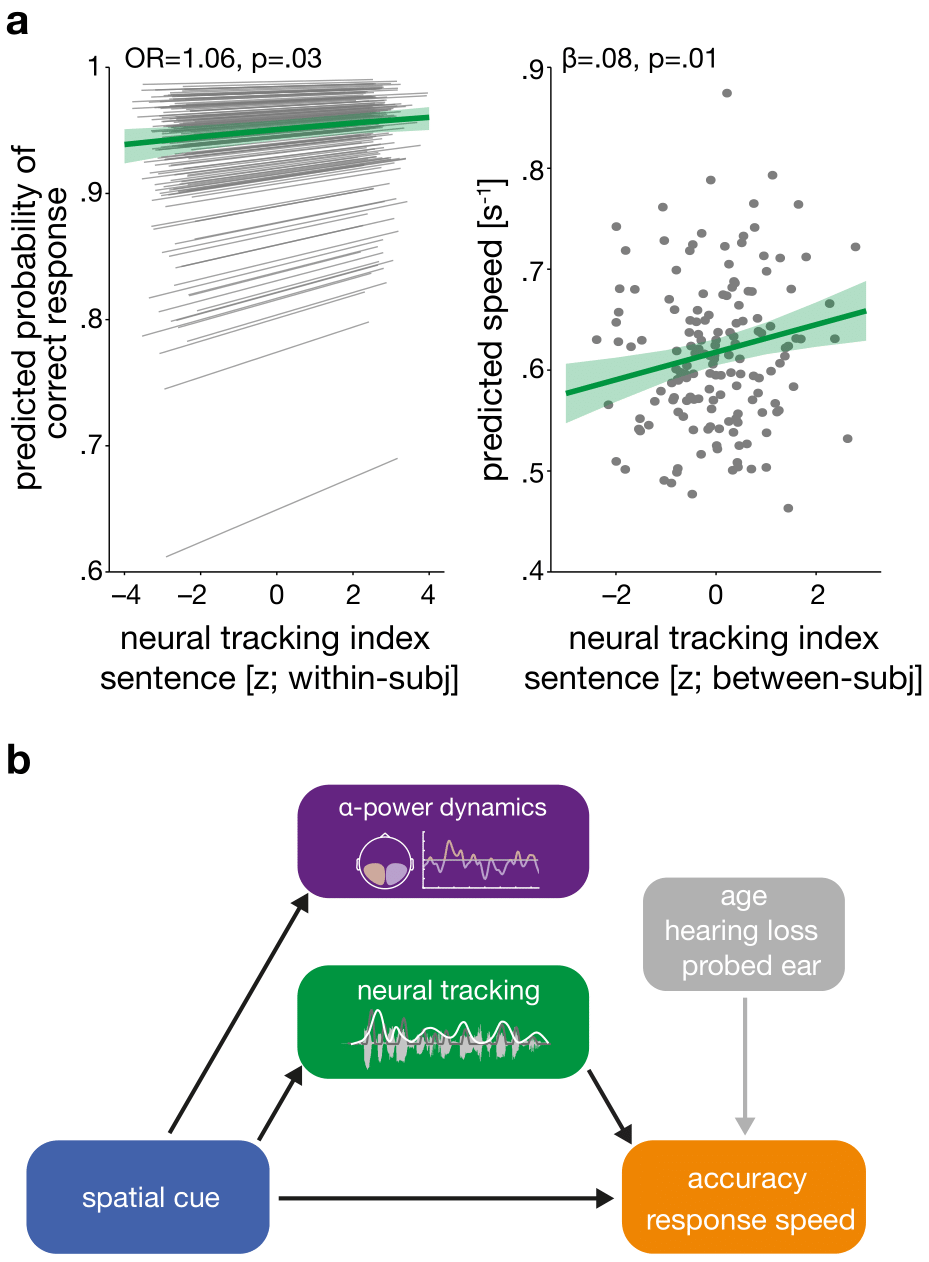
Out now in eLife: Obleserlab stats modelling wiz Sarah Tune together with Jonas has just published a serious statistical piece of evidence on how, in our >N=100 cohort of ageing listeners as funded by the European Research Council, neural signatures of attentive listening and the actual behavioural outcome a listener achieves are not trivially connected, and in fact are not even predictive of one another – when we look at the longitudinal, two-year trajectory that listeners exhibit in both measures over time.
This study (here is a brief eLife digest on it) poses a keystone result to the ERC project “AUDADAPT”, which we now continue with other projects and spin-offs. Many thanks to the large group of Lübeck citizens who continue to support us with their precious time and their brain and behavioural data!
Diese Studie (hier ist eine kurze eLife-Zusammenfassung) ist ein Schlüsselergebnis des ERC-Projekts “AUDADAPT”, das wir nun mit anderen Projekten und Spin-offs fortsetzen. Vielen Dank an die große Gruppe von Lübecker Bürgerinnen und Bürgern, die uns weiterhin mit ihrer kostbaren Zeit und ihren Gehirn- und Verhaltensdaten unterstützen!