We are proud to announce that PhD student Julia Erb just came out with a paper issued in Journal of Neuroscience:
The Brain Dynamics of Rapid Perceptual Adaptation to Adverse Listening Conditions
Grab it here:
- The Journal of Neuroscience, 26 June 2013, 33(26): 10688–10697; doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4596–12.2013
- Abstract / Full Text
- Full Text (PDF)
Abstract:
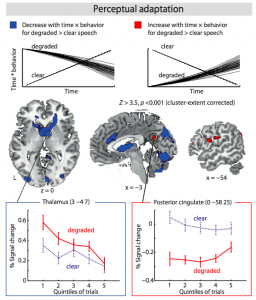
Listeners show a remarkable ability to quickly adjust to degraded speech input. Here, we aimed to identify the neural mechanisms of such short-term perceptual adaptation. In a sparse-sampling, cardiac-gated functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) acquisition, human listeners heard and repeated back 4‑band-vocoded sentences
References
- Erb J, Henry MJ, Eisner F, Obleser J. The brain dynamics of rapid perceptual adaptation to adverse listening conditions. J Neurosci. 2013 Jun 26;33(26):10688–97. PMID: 23804092. [Open with Read]