Objectives:
Psychoacoustic tests assessed shortly after cochlear implantation are useful predictors of the rehabilitative speech outcome. While largely independent, both spectral and temporal resolution tests are important to provide an accurate prediction of speech recognition. However, rapid tests of temporal sensitivity are currently lacking. Here, we propose a simple amplitude modulation rate discrimination (AMRD) paradigm that is validated by predicting future speech recognition in adult cochlear implant (CI) patients.
Design:
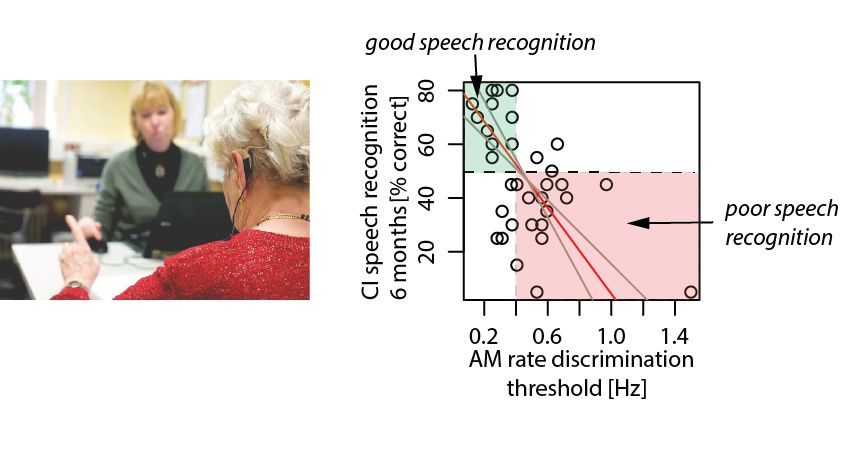
In 34 newly implanted patients, we used an adaptive AMRD paradigm, where broadband noise was modulated at the speech-relevant rate of ~4 Hz. In a longitudinal study, speech recognition in quiet was assessed using the closed-set Freiburger number test shortly after cochlear implantation (t0) as well as the open-set Freiburger monosyllabic word test 6 months later (t6).
Results:
Both AMRD thresholds at t0 (r = –0.51) and speech recognition scores at t0 (r = 0.56) predicted speech recognition scores at t6. However, AMRD and speech recognition at t0 were uncorrelated, suggesting that those measures capture partially distinct perceptual abilities. A multiple regression model predicting 6‑month speech recognition outcome with deafness duration and speech recognition at t0 improved from adjusted R2 = 0.30 to adjusted R2 = 0.44 when AMRD threshold was added as a predictor.
Conclusions:
These findings identify AMRD thresholds as a reliable, nonredundant predictor above and beyond established speech tests for CI outcome. This AMRD test could potentially be developed into a rapid clinical temporal-resolution test to be integrated into the postoperative test battery to improve the reliability of speech outcome prognosis.